[無料ダウンロード! √] s p d f orbitals shapes in hindi 322578-S p d f orbitals shapes in hindi
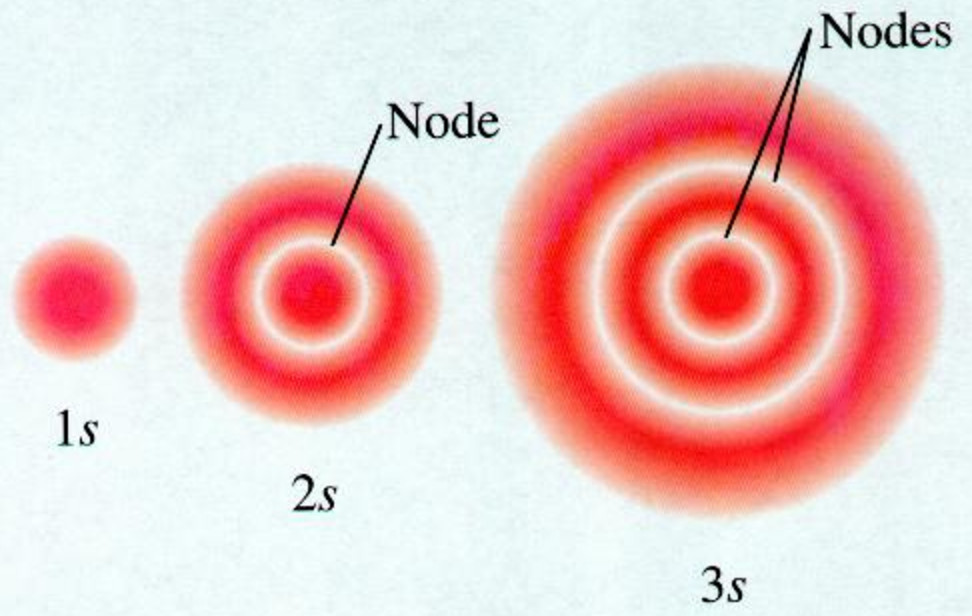
These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one nodeChemistry Electron Configuration s,p,d,f Orbitals 1 Answer shr Nov 3, 16 The orbital shapes vary from s, p, d and f, they represent the most likely area of finding an electron Explanation These are the shapes that are related with the four quantum numbers of the last electron Answer linkClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties homework assignment help is most useful online help portal for the students that providing all Online spdf Block Elements assignment help ServicesIn the long form of the periodic table, elements are grouped into four main blocks, purely on the basis of electronic configurationsElements are grouped in blocks 's', 'p', 'd' and 'f

Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures
S p d f orbitals shapes in hindi
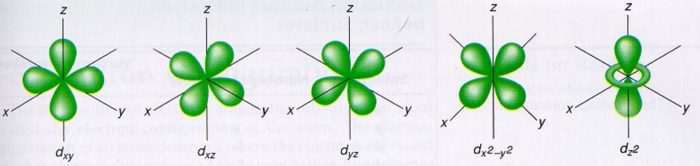
S p d f orbitals shapes in hindi-This is an f orbital It is oriented in 7 different ways and each orientation can hold 2 electrons Therefore f orbitals together have 7 degenerates and hold 14 electrons So these are the images of d and f orbitals If you wanted to see a real dThe porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;



How To Write S P D F Electron Configuration For Carbon Nitrogen And Oxygen Electron Configuration Oxygen Chemistry Lessons
For a d orbital, draw a fourleafed clover;Shapes of s p and d orbitals S, p and dwhether we are talking about an s, p, d or f orbital It also determines the orbital angular momentum of the electron as it spins round the nucleus This happens to be the shape of methane, and so sp3 hybrids are a plausibleOrbitals characteristic shapes of s p and d orbitals Periodic table and quantumThe #f# orbitals in the same quantum level have less radial nodes than other orbitals of lower angular momentum #l# (where the function dips down to #y = 0# on the above graph) In contrast, these also have more angular nodes than the #d#, #p#, and #s# orbitals in the same quantum level (not seen in the above graph), as they have the highest #l
In this Chemistry video in Hindi for class 11 we explained the shape of dorbital from the topic 'Shapes of Atomic Orbitals' And we also explained radial noThe subshells have four types s, p, d, and f, and each subshell has a specific number of orbitals with different shapes This is determined by the magnetic quantum number This is determined byS Orbital Versus P Orbital While orbital numbers (eg, n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time The smallest sphere is 1s
Footnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellFootnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellAll s orbitals are spherical in shape but differ in size, which increases as the principal quantum number increases The radial probability distribution for the 1s orbital exhibits a maximum at 529 pm (0529 ) from the nucleus There is a p subshell in every shell for which n ≥ 2, and each p subshell contains three p orbitals that are



How To Write S P D F Electron Configuration For Carbon Nitrogen And Oxygen Electron Configuration Oxygen Chemistry Lessons



Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
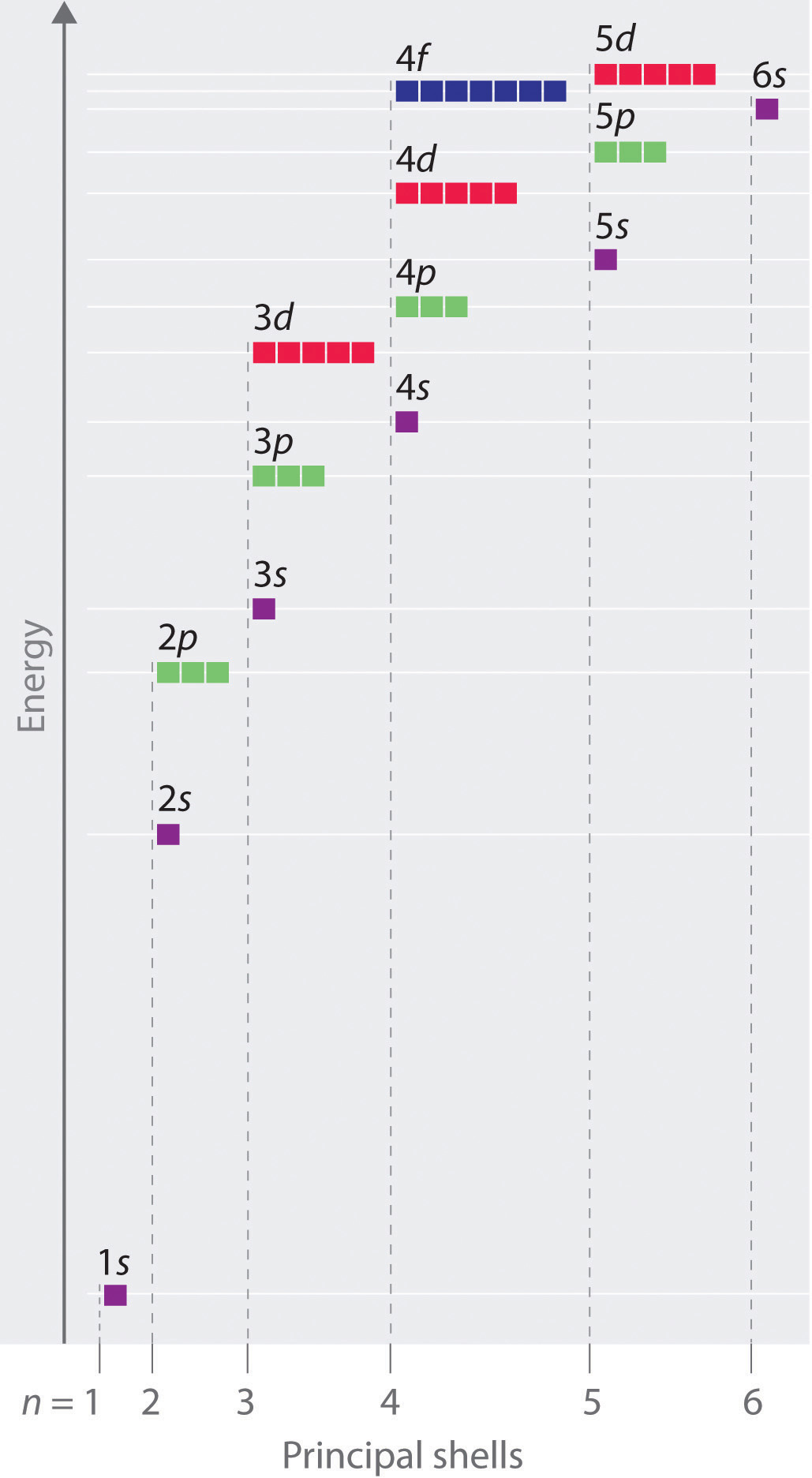
Because the order of electron penetration from greatest to least is s, p, d, f;These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one nodeFor an f orbital, see below An s orbital is a sphere In two dimensions, we draw it as a circle A p orbital consists of two lobes of electron density on either side of the nucleus We usually draw p orbitals as figure eights, but we should remember p orbitals are really much


Difference Between Atomic Orbital And Molecular Orbital Definition Characteristics Properties



Atomic Orbital Shape And Orientation Magnetic And Spin Quantum Number Ii Ashwin Sir Golectures Online Lectures
Shapes Of S P And D Orbitals Pdf Download >>> DOWNLOAD (Mirror #1) d9ef92e1f7 embarkation card japan pdf downloadlouis claude fillion pdf downloadthe soul's code pdf downloadtoeic 4n4 860 level pdf downloadthe columbian exchange and global trade pdf downloadmcconnell economics 19th edition pdf free downloadghostgirl christmas spirit pdf downloadmanierismo y barroco pdf downloadcefaleaThe order of the amount of shielding done is also in the order s, p, d, f Since the 2s electron has more density near the nucleus of an atom than a 2p electron, it is said to shield the 2p electron from the full effective charge of the nucleusAnswer to Describe the shapes of s p and d orbitals How arc these orbitals related to the quantum numbers n, t, and ml?



Chem Xi 2 08 Shapes Of Orbitals Electronic Configuration 17 Pradeep Kshetrapal Physics Channel Youtube



Shapes Of Orbitals Shape Of S Orbital P Orbital D Orbital F Orbital Node Angular Node Youtube
Atomic orbitals s, p, d, and f The s orbital is spherical in shape;The nucleus resides at the center of the sphere It does not orient itself in any direction In other words, it is nondirectional There are three dumbbellshaped p orbitals Each orbital has two lobes aligned in one of the three axesThe order of the amount of shielding done is also in the order s, p, d, f Since the 2s electron has more density near the nucleus of an atom than a 2p electron, it is said to shield the 2p electron from the full effective charge of the nucleus



What Is The Difference Between Shell Subshell And Orbital Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Blogs Tutorials Digital Kemistry Youtube
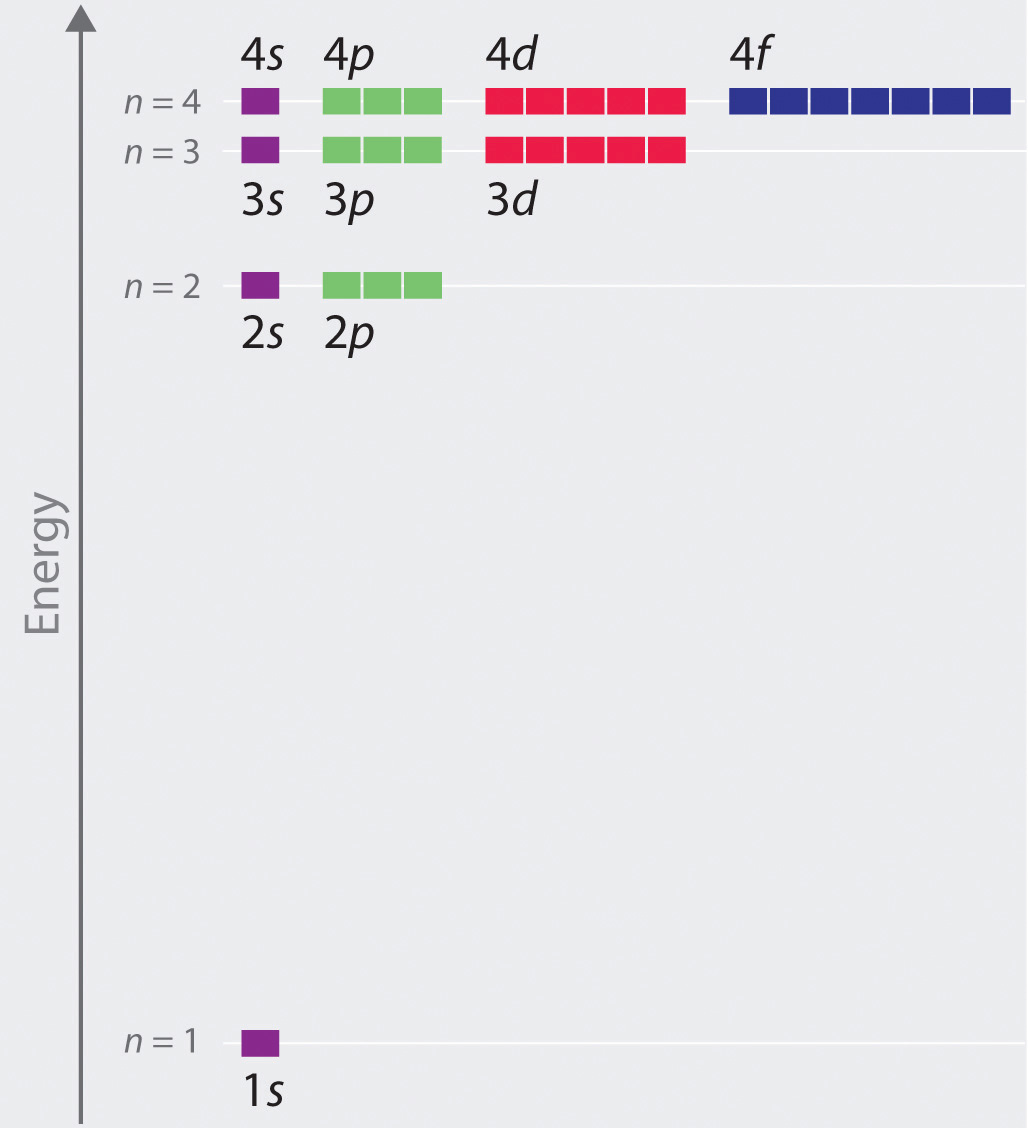


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts
Shapes Of S P And D Orbitals Pdf Download >>> DOWNLOAD (Mirror #1) d9ef92e1f7 embarkation card japan pdf downloadlouis claude fillion pdf downloadthe soul's code pdf downloadtoeic 4n4 860 level pdf downloadthe columbian exchange and global trade pdf downloadmcconnell economics 19th edition pdf free downloadghostgirl christmas spirit pdf downloadmanierismo y barroco pdf downloadcefaleaThe s, p, d, and f stand for sharp, principal, diffuse and fundamental, respectively The letters and words refer to the visual impression left by the fine structure of the spectral lines which occurs due to the first relativistic corrections, espThe orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals Electrons fill orbitals with the lowest energy level possible first THIS WEEK WE WILL f orbitals have an intricate shape



What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Part 2 P Orbital Chemistry For Class 11 In Hindi Youtube
Orbital Shapes (s, p, d and f) Explanation The proposed tetrahedral nucleus structure , along with rules for proton spin alignment that is the cause of the repelling force used to calculate orbital distances , can explain the shapes of the s, p, d and f orbitals2dxy, 3dxz, 3dyz, 3d(xy)^2 and 3dz^2SHAPES OF ATOMIC ORBITALS S, P, D and F



What Is The Difference Between An Orbit And An Orbital Quora



D Orbitals Shape Nodal Planes In D Orbitals Eminent Guide Qmm L 23 Youtube
Orbitals ChemistryWhat are Atomic Orbitals?Atomic orbitals are mathematical functions that describe the wave nature of electrons (or electron pairs) in an atF Orbital The sequence for the f block is unique Beginning with lanthanum (Z=57) it starts a block that contains 15 elements The 5 th level of a tetrahedron has 15 units There are 15 elements for the f block (Z=57 to 71), although an odd number affects the number of orbitals (14 / 2 = 7) It converts a proton to neutron in the next d block to compensate, beginning with the 5d block2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,



What Is The Difference Between Shell Subshell And Orbital Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Blogs Tutorials Digital Kemistry Youtube



Quantum Number Chemistry Class 11th Trick For Quantum Numbers Quantum Number By M M Education
Describe the shapes and relative energies of the s, p, d, and f atomic orbitals vscogirl vscogirl 12//19 Chemistry Middle School 47 Describe the shapes and relative energies of the s, p, d, and f atomic orbitals 1 See answer vscogirl is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points oyinade oyinadeAtomic orbitals s, p, d, and f The s orbital is spherical in shape;In the fourth and fifth energy levels Nitrogen



Electronic Configuration Stability Of Sub Shells Structure Of Atom Dr Rajeev Ranjan By Neetprep Neet Preparation


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts
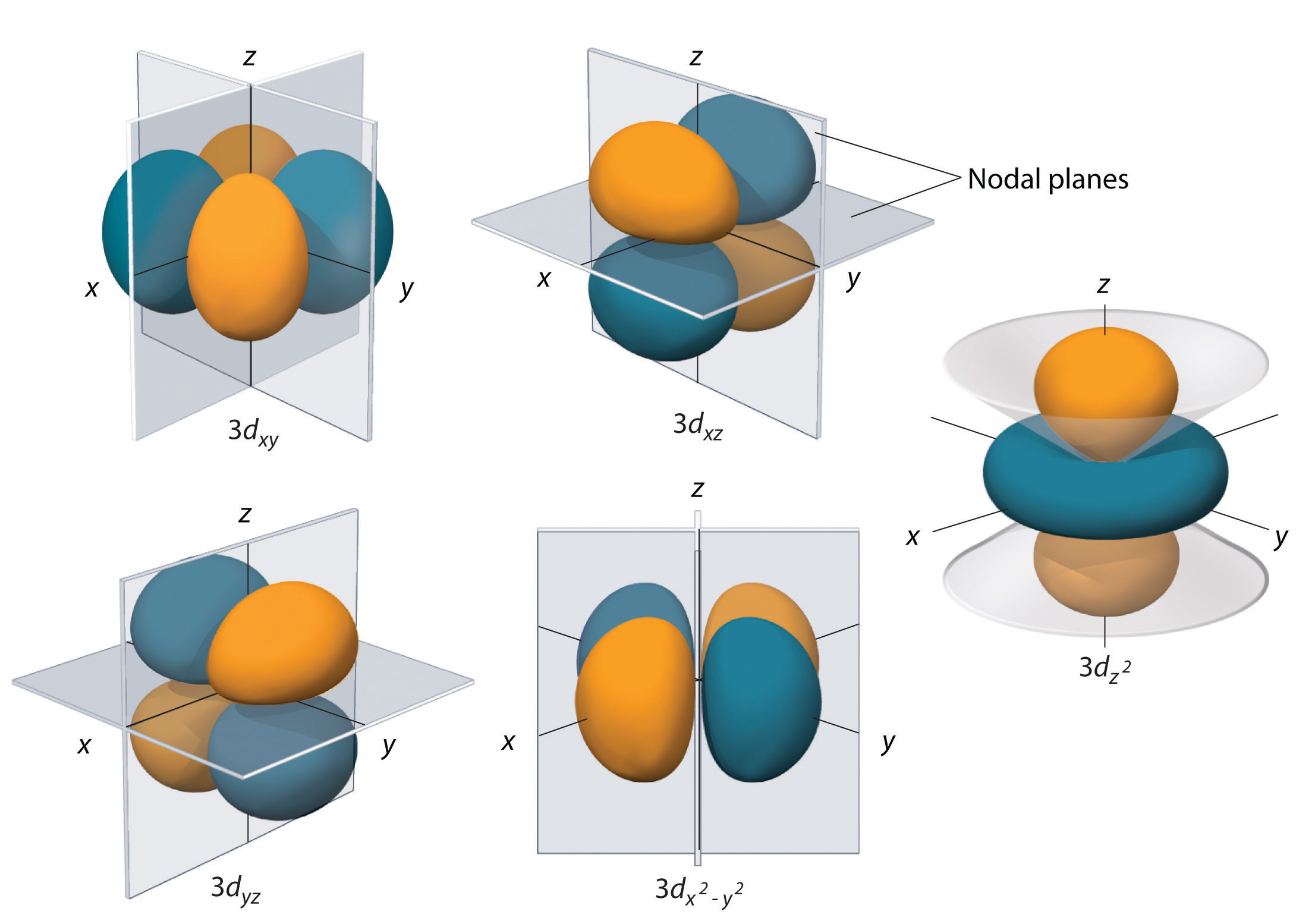
An sorbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a porbitals is dumbbellshaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped The fifth d orbital is shaped like an elongated dumbbell with a doughnut around its middle The orbitals in an atom are organized into different layers or electron shellsF Orbital The sequence for the f block is unique Beginning with lanthanum (Z=57) it starts a block that contains 15 elements The 5 th level of a tetrahedron has 15 units There are 15 elements for the f block (Z=57 to 71), although an odd number affects the number of orbitals (14 / 2 = 7) It converts a proton to neutron in the next d block to compensate, beginning with the 5d blockF orbitals their shapes are even more complex than s, p, or d orbitals;



Orbitals By 3dhubplayer



S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
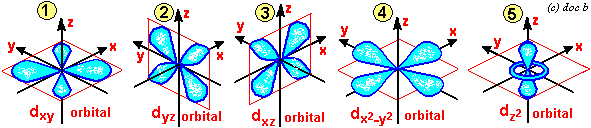
Therefore, we can say that there are about 3 p orbitals whose axes are mutually perpendicular Just like the s – orbitals, with an increase in size and energy of p orbitals quantum number ( 4p > 3p > 2p ), the size and energy of p orbitals also increase D – Orbitals Magnetic orbital quantum number for d orbitals is given as ( 2, 1, 0, 1The porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;For a p orbital, draw a figure eight;



Electron Orbitals S P D 3gp Mp4 Hd Download


Shapes Of Atomic Orbital Chemistry Class 11 Structure Of Atom
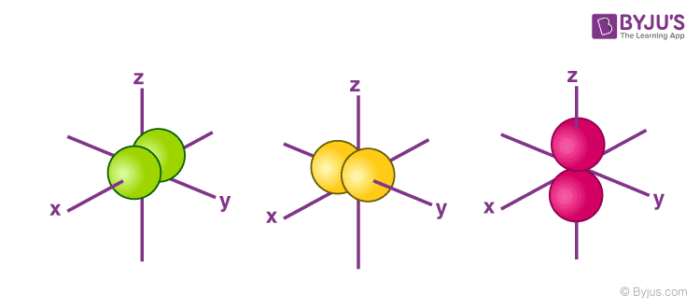
For example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2D and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals that become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are nine totalThe nucleus resides at the center of the sphere It does not orient itself in any direction In other words, it is nondirectional There are three dumbbellshaped p orbitals Each orbital has two lobes aligned in one of the three axes



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures
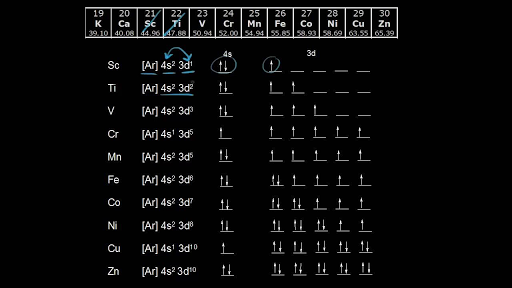


Electron Configurations Of The 3d Transition Metals Video Khan Academy
S Orbital Versus P Orbital While orbital numbers (eg, n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time The smallest sphere is 1sClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties homework assignment help is most useful online help portal for the students that providing all Online spdf Block Elements assignment help ServicesIn the long form of the periodic table, elements are grouped into four main blocks, purely on the basis of electronic configurationsElements are grouped in blocks 's', 'p', 'd' and 'fFor example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures



S P D F Obitals Notation Shapes Diagrams How To Work Out Electron Arrangements Configurations Order Of Filling Quantum Levels Electronic Structure Of Atoms Gce A Level Revision Notes
Relative probability is indicated by a series of dots, indicating the "electron cloud" 90% electron probability/cloud for 1s orbital (notice higher probability toward the centre) p orbitals and d orbitals p orbitals look like a dumbell with 3 orientations px, py, pz ("p sub z") Four of the d orbitals resemble two dumbells in a cloverAtomic orbitals s, p, d, and f The s orbital is spherical in shape;Can hold a total of 14 electrons in 7 subshells;



Shapes Of Orbitals What Is Orbital Types Of Orbitals



Shapes Of Orbitals S P D And F Orbitals Shape Urdu Hindi Youtube
Chemistry Electron Configuration s,p,d,f Orbitals 1 Answer shr Nov 3, 16 The orbital shapes vary from s, p, d and f, they represent the most likely area of finding an electron Explanation These are the shapes that are related with the four quantum numbers of the last electron Answer linkBecause the order of electron penetration from greatest to least is s, p, d, f;Fred Senese of Antoine Frostburg explains "You might expect that the 's' stands for 'spherical' and 'p' stands for 'polar' because these imply the shapes of the s and p orbitals, but unfortunately, the letter designations have nothing to do with



Part 5 Shapes Of The Atomic Orbital S P D And F Orbital Atomic Structure Youtube



Atomic Structure
The nucleus resides at the center of the sphere It does not orient itself in any direction In other words, it is nondirectional There are three dumbbellshaped p orbitals Each orbital has two lobes aligned in one of the three axesTHE d ORBITALS In the third energy level, five d orbitals are present They have complicated names and shapes The 3s and 3p (3px, 3py 3px) are present too A total of nine orbitals are found in the third energy level The five 3d orbitals are named;The symmetry of s orbitals along three axes x,y,z Between two regions of the high probability of electrons is a spherical node, it is the region where the probability of finding electrons is zero Click NCERT Class 11 Chemistry for free demos and animated video lectures The p Orbital The maximum value of l is n – 1, so the only levels with n = 2 or higher have a p orbital 2p orbital is


Q Tbn And9gcrjaqjlb8lpy2zmnxb7djnungtx4z3mbsdjg7v7iofb5bmcmoq Usqp Cau
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;Orbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry Learn more about atomic orbital at Byjus2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,


Q Tbn And9gcqulzhcplpqcomqengxsfh8zlrg Jw3 8b 3am6v0f U Tzuel Usqp Cau



Electron Orbital Definition Shells And Shapes In Hindi Hindi Understanding Atom And Atomic Structure Unacademy
S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;For an s orbital, draw a circle;



Surface Tension And Viscosity Class 11 Chemistry Urdu Hindi Fluid Me Surface Tension 11th Chemistry Chemistry



Shapes Of Orbitals S P D And F Orbitals Shape Urdu Hindi Youtube
/ShellAtomicModel-5a6ab592aded4bb7a1328f809e4f10da.jpg)


The Aufbau Principle Definition Rules And Exceptions



Si Units Basic Chemistry In Hindi Part 1 Chemistry Innovative Education Chemistry Notes



Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



Electronic Configuration Of Atoms W3spoint



Electronic Vinyas Formula In Hindi



What Is The Difference Between Molecular And Atomic Orbitals Quora
/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Quantum Number Wikipedia



Electron Configuration Wikipedia



What Is The Shape Of An F Orbital Quora



What Is The Difference Between Shell Subshell And Orbital Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Blogs Tutorials Digital Kemistry Youtube



What Are Shells Sub Shells Orbitals Submarine Chemistry Video Lessons



Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital


Q Tbn And9gcthkbfxsvcmd3slqsueqeacalyhgywzqc Gx3p0kkc4ifvl6ry Usqp Cau


S P D Block Periodic Table Periodic Table Timeline



In Hindi Orbital Shape Of S P D Orbitals Iit Jee Hindi Atomic Structure Iit Jee Unacademy



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts


Shapes Of Atomic Orbital Chemistry Class 11 Structure Of Atom



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
/atomic-nucleus-and-orbiting-electrons-475158093-58ebfd365f9b58ef7ead201c.jpg)


Orbital Definition And Example


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



Spdf कक षक क आक त य Shape Of Spdf Orbitals In Hindi Youtube



What Is The Difference Between An Orbit And An Orbital Quora


What Is The Difference Between Molecular And Atomic Orbitals Quora


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



Orbital Chemistry And Physics Britannica



What Is The Difference Between An Orbit And An Orbital Quora
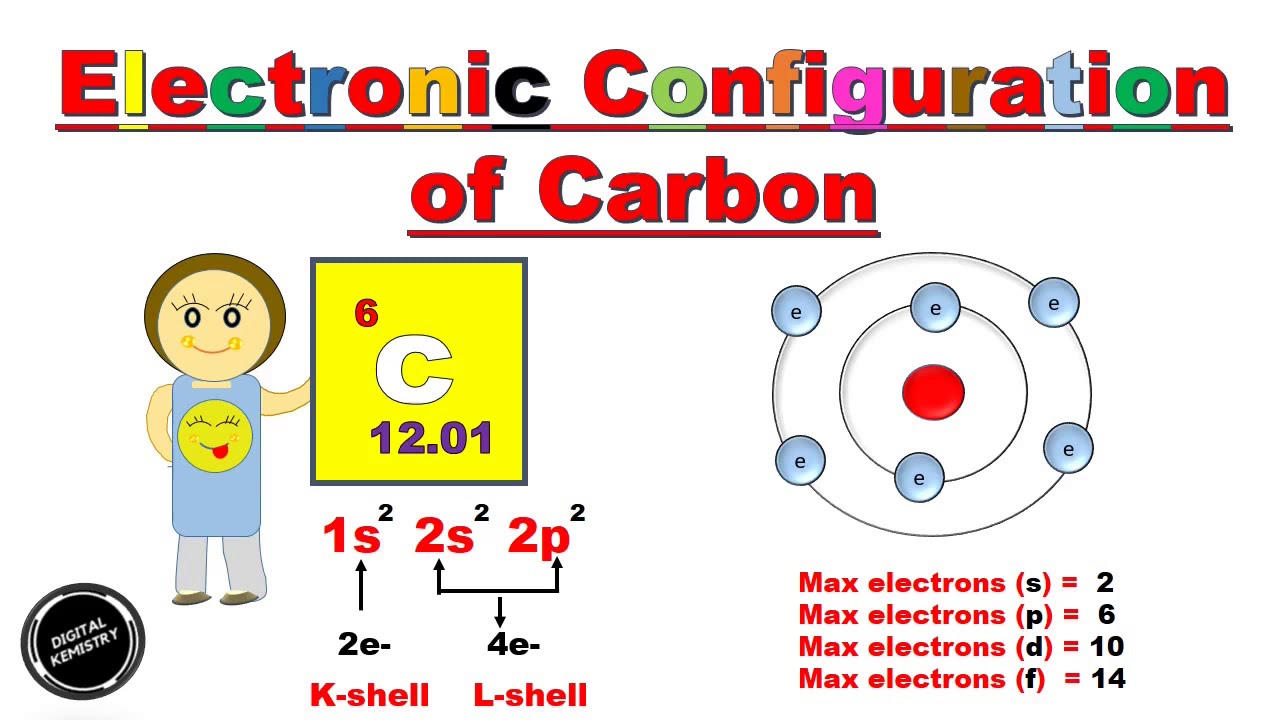


S P D F Electronic Configuration Of Carbon In Hindi Urdu Structure Of Carbon Atom Youtube


Using S P D F Notations Describe The Orbital With The Following Quantum Numbers A N 2 L 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Quantum Numbers For The First Four Shells Video Khan Academy


Spdf Drone Fest



Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals Explained S Sp Sp2 And Sp3 Organic Chemistry Youtube Golectures Online Lectures
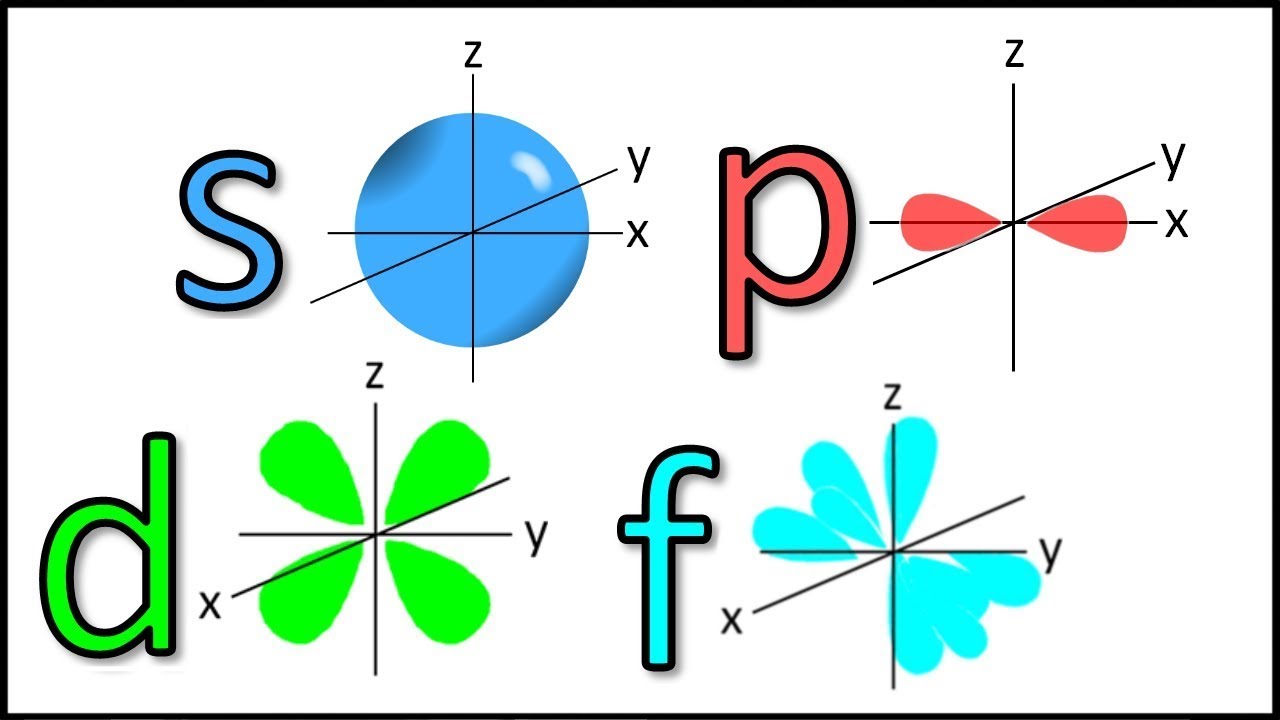


Atomic Orbitals And Its Shape Atomic Structure 11th Jee Neet Board In Hindi Youtube
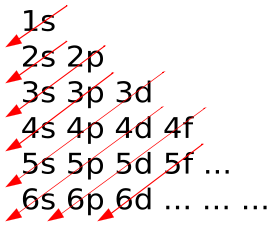


The Building Up Aufbau Principle Introduction To Chemistry
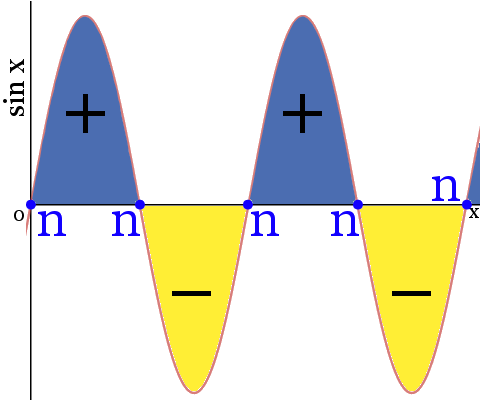


Definition Of Orbital Nodes Chemistry Dictionary



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures



Shells Subshells And Orbitals Video Khan Academy



Shape Of S Orbital In Hindi Chemistry Video Lectures



Atomic Orbitals In Hindi Orbit And Orbital In Hindi Difference Between Orbit And Orbital S P D Youtube
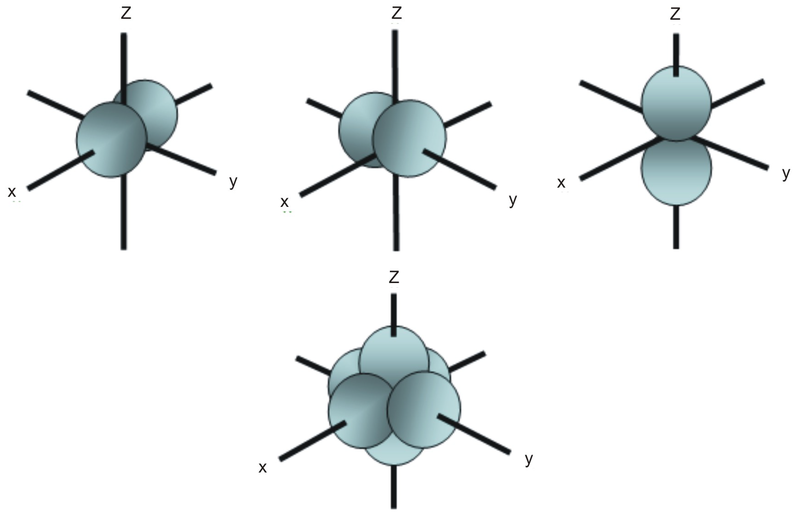


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


What Is Names Of F Orbitals Quora



S Orbital And P Orbital Shape Nodal Planes In Orbitals Eminent Guide Qmm L 22 Youtube



Chapter 7 Handout 1 Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers Principal



Shapes Of Orbitals Of An Atom


What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora


Spdf Drone Fest



Important Notes For Ncert Chemistry Class 11 Shapes Of Orbital



Shapes Of Orbitals Of An Atom


Spdf Drone Fest
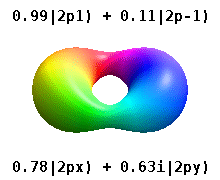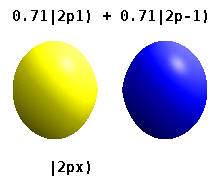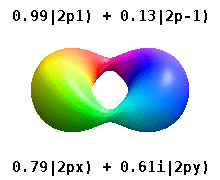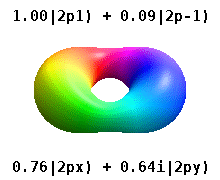


Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
/GettyImages-117451436-56a133b63df78cf7726859ff.jpg)


Subshell Definition For Electrons


Difference Between Shell Subshell And Orbital Definition Structure Properties
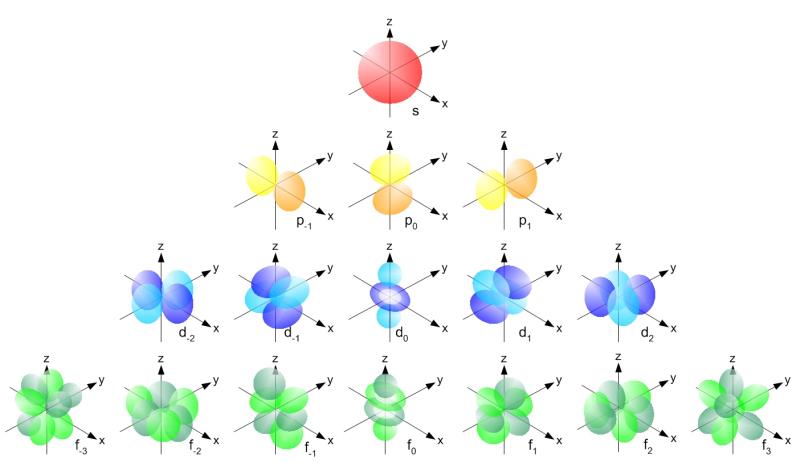


Can U Give Me A Proper Explanation Of Spdf Configuration Edurev Class 11 Question
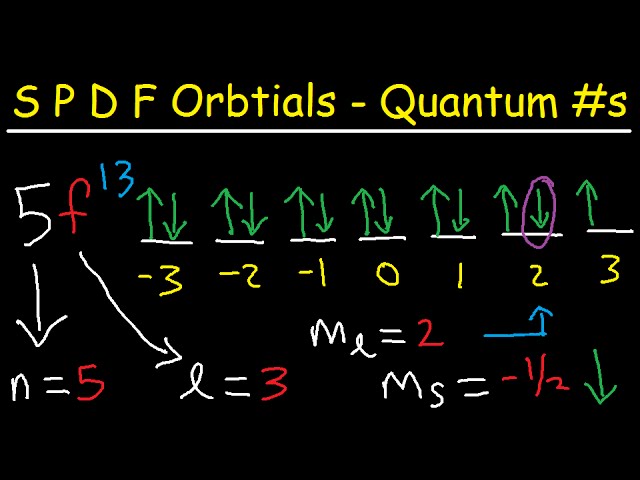


S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube



Electronic Vinyas Formula In Hindi



Shapes Of S P D Orbitals English Hindi Youtube
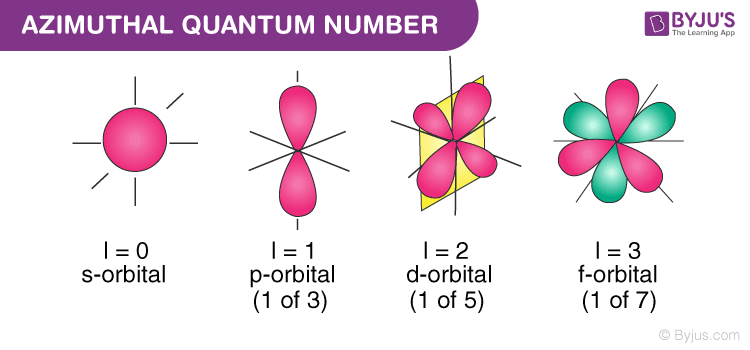


Azimuthal Quantum Number Definition Magnetic Quantum Number



What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora



Molecular Orbital Theory Bonding Anti Bonding Mo Chemical Bonding Molecular Theories Chemistry


1



Electron Orbital Definition Shells And Shapes In Hindi Hindi Understanding Atom And Atomic Structure Unacademy
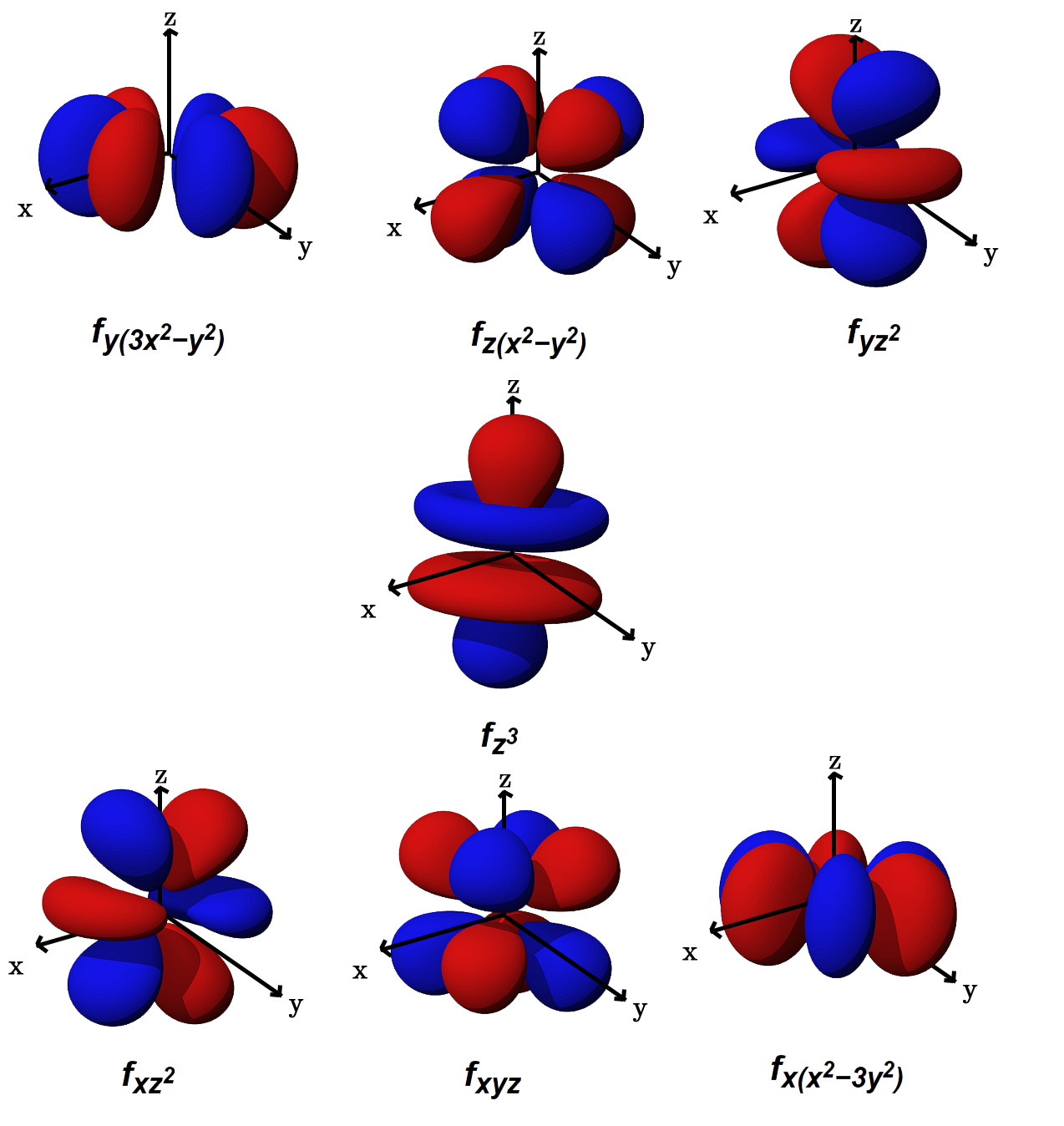


What Is The Shape Of F Orbital Example



Atomic Orbital Wikipedia



Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Part 3 D Orbital Chemistry For Class 11 In Hindi Youtube
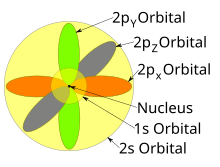


Atomic Orbital Wikipedia


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
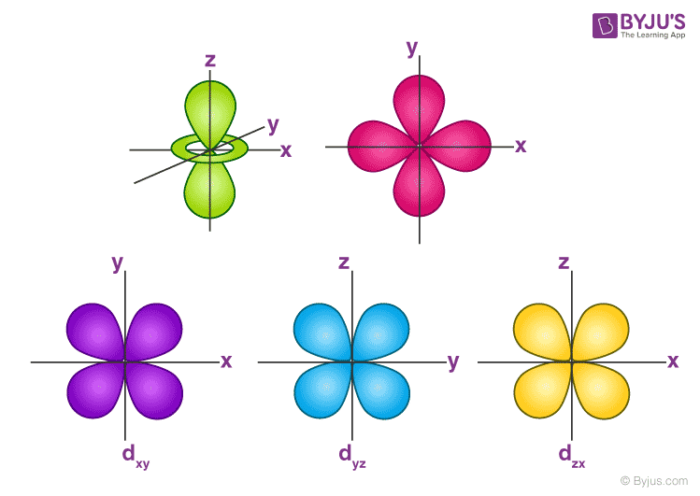


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital


コメント
コメントを投稿